Introduction of HTML
HTML is a hypertext markup language.
HTML is the most commonly used markup language for creating Web pages.
A markup language provides a way to describe the structure of text-based information on a Web pages.Hypertext is similar to regular text.
HTML is designed by w3c (world wide web consortium) is an organization.
USES OF HTML IN MARKET
In google
Online shop ex: flipkart,amazon,.snapdeal,etc...
Business
organization
Education
Research center
Creating and Saving HTML Document
We can create a HTML Document using a text editor, like Notepad, adding our html code to the document, and saving it with filename.html extension.
The following step to create and save an html document:
Step1: Start->All program->Accessories->Notepad.
Step2: The Notepad window opens with blank document.
Step3: Add the html code in the document.
Step4: click File->Save As
Step5: Save As dialog box appear and saving the document inside folder filename.html and click ok.
Opening the html document in a web Browser
The following step to open an html document:
Step1: Open the folder contain our html document.
Step2: Double click the html document.html document will open in the default web browser in our computer.
HTML ADVANTAGE
Don't require additional software to run HTML.
It can be run in normal web browser. for example: Internet Explorer,Mozilla Firefox,Opera etc...
First Look at HTML
In case of HTML is more important of show the text in web browser using basic tags.
An HTML tag is format of a pair of angle brackets (<tag>) text place in this bracket.
That angle brackets defines an HTML element .
HTML element have two properties
1. Attributes(ex: <img align='left'>) : align is the attribute
2. Content
syntax: <element-name> content </element-name>
for example:
<strong> hello </strong>
In above example hello is a called of content.
Basic structure of an HTML document
The basic structure of HTML
syntax:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html>
<body>
Content of the web page
</body>
</html>
example:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html>
<body>
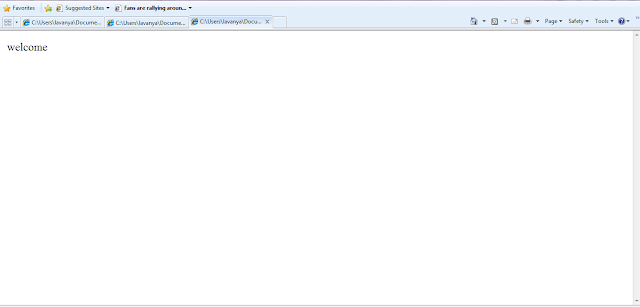
welcome
</body>
</html>
Result:
The result of web page welcome
2. dir
Dir is a gives the direction of the text.
we can set this attribute of text direction
3. id
The id attribute is used to set the unique name for the element & used for referring to it.
4. lang
The lang attribute is used for base language for the element.
5. profile
Gives the location of one or more white-space separated metadata profile URLs for the current document.
6. style
The style attribute is used to add style sheet information directly to a tag.
7. title
The title is used to provide advisory text about an element or its contents.
1. <base>
Base URL for the document.
2. <Basefont>
Basefont for the document.
3.<bgsound>
Background sound.
4. <isindex>
Rudimentary input control.
5. <link>
Link are use to connect one page to another.
6. <meta>
It gives the header information.
7. <nextid>
Hint for the name value to use when creating a new hyperlink element.
8. <noscript>
Holds text that only appears if the browser does not support the <script> element.
9 .<script>
Holds programming script statements, like javascript.
10. <style>
Includes style information for rendering.
11 .<title>
The title of the web page that appears in the web browser.
Each <head> element should contain a <title> element.
Attributes of the <title> Element:
2. dir
Dir is a gives the direction of the text.
we can set this attribute of text direction
The lang attribute is used for base language for the element.
3. style
The style attribute is used to add style sheet information directly to a tag.
Content of the web page
</body>
</html>
example:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html>
<body>
welcome
</body>
</html>
Result:
The result of web page welcome
Title of web page
syntax:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html>
<head>
<title>
Title of the web page
</title>
</head>
<body>
Content of the web page
</body>
</html>
example:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html>
<head>
<title> html </title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> welcome </h1>
<p> The <b><i><u> html<u><i><b> is hypertext markup language. It is used to create a web page.A markup language provides a way to describe the structure of text-based information on a web page.</p>
<hr>
</body>
</html>
Result:
The preceding example uses some of the most common element found in HTML document:
</title>
</head>
<body>
Content of the web page
</body>
</html>
example:
<!DOCTYPE>
<html>
<head>
<title> html </title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> welcome </h1>
<p> The <b><i><u> html<u><i><b> is hypertext markup language. It is used to create a web page.A markup language provides a way to describe the structure of text-based information on a web page.</p>
<hr>
</body>
</html>
Result:
The preceding example uses some of the most common element found in HTML document:
- <!DOCTYPE> indicates the particular version of html being used in the document.but that tag not used mostly.
- <html>,<body>,<head>tag pair are used to specify the general structure of the document.
- <title> and </title> tag pair specifies the title of the document.It appear in the title bar of the web browser.
- <h1> and </h1> is called header tag pair.It creates a headline to indicate some important information.
- <hr> tag is used to only inserts a horizontal rule, or bar,across the screen.
- <p> and </p> is called paragraph tag.It is used to create a paragraph of text.
- <u></u> is used for underline the text within opening and closing tags.
- <i></i> is used to italic style for the text within opening and closing tags.
- <b></b> is used to bold style for the text within opening and closing tags.
<HTML> Tag
The <html> tag place on the beginning and the end of an HTML document.It is also called the root element.
The <html> tag, directly contains only the <head> tag, the <body> tag, and <frameset> tag instead of <body>tag.
The <html>tag's used in a document, as a container for all other elements.
<HTML>ELEMENT
Attributes:
- dir
- id
- lang
- version
- xmlns
1. class Attribute
The class attribute is used to indicate the class. It belongs to id, class is used to associate a tag with a name.
2. dir Attribute
Dir is a gives the direction of the text.
we can set this attribute of text direction
3. id Attribute
The id attribute is used to set the unique name for the element & used for referring to it.
4.lang Attribute
The lang attribute is used for base language for the element.
5.version Attribute
Indicate the version of the language used.
6.xmlns Attribute
It is used for declare a namespace for custom tags in an html document.
2. dir Attribute
Dir is a gives the direction of the text.
we can set this attribute of text direction
- "ltr"-left to right
- "rtl"-right to left
3. id Attribute
The id attribute is used to set the unique name for the element & used for referring to it.
4.lang Attribute
The lang attribute is used for base language for the element.
5.version Attribute
Indicate the version of the language used.
6.xmlns Attribute
It is used for declare a namespace for custom tags in an html document.
The <HEAD> Element
The information in the head of an HTML document is very important because it is used to describe or augment the content of the document.
The information contained with in the <head> tag is information about information of the page, which generally of referred to as meta-information.
Attributes of the< head> element:
- class
- id
- dir
- lang
- profile
- style
- title
1. class
The class attribute is used to indicate the class. It belongs to id, class is used to associate a tag with a name.2. dir
Dir is a gives the direction of the text.
we can set this attribute of text direction
- "ltr"-left to right
- "rtl"-right to left
3. id
The id attribute is used to set the unique name for the element & used for referring to it.
4. lang
The lang attribute is used for base language for the element.
5. profile
Gives the location of one or more white-space separated metadata profile URLs for the current document.
6. style
The style attribute is used to add style sheet information directly to a tag.
7. title
The title is used to provide advisory text about an element or its contents.
Elements to be added to the <head> Element:
- <base>
- <basefont>
- <bgsound>
- <isindex>
- <link>
- <meta>
- <nextid>
- <noscript>
- <script>
- <style>
- <title>
1. <base>
Base URL for the document.
2. <Basefont>
Basefont for the document.
3.<bgsound>
Background sound.
4. <isindex>
Rudimentary input control.
5. <link>
Link are use to connect one page to another.
6. <meta>
It gives the header information.
7. <nextid>
Hint for the name value to use when creating a new hyperlink element.
8. <noscript>
Holds text that only appears if the browser does not support the <script> element.
9 .<script>
Holds programming script statements, like javascript.
10. <style>
Includes style information for rendering.
11 .<title>
The title of the web page that appears in the web browser.
The <title> Element
The <title> element contains the title of the HTML document. It will appear in the title bar of the web browser.Each <head> element should contain a <title> element.
Attributes of the <title> Element:
- class
- dir
- lang
- style
1. class
The class attribute is used to indicate the class. It belongs to id, class is used to associate a tag with a name.2. dir
Dir is a gives the direction of the text.
we can set this attribute of text direction
- "ltr"-left to right
- "rtl"-right to left
The lang attribute is used for base language for the element.
3. style
The style attribute is used to add style sheet information directly to a tag.
The <BODY> Element
The <body> element contains the body of the HTML document. The element include the entire content that will appear in the web browser.
It can include text, images, and multimedia element.
Attributes of the <body> Element:
- alink
- background
- bgcolor
- bgproperties
- bottommargin
- class
- id
- dir
- lang
- language
- leftmargin
- link
- marginheight
- marginwidth
- rigthmargin
- scroll
- style
- text
- title
- topmargin
- vlink
1. alink
It is used to color of the hyperlinks when you are clicked;
You can set this attribute to a predefined color or a color value.
2. background
The element used to set the background image.
3. bgcolor
The color of the background of the browser; you can set this attribute to a predefined color or a color value.
4.bgproperties
Indicate if the background should scroll when the text scrolls;
If you set this attribute to fixed; It is only allowed value, the background will not scroll when the text scrolls.
5. bottommargin
It specifies the bottom margin, which is the empty space at the bottom of the document.
6. class
The class attribute is used to indicate the class. It belongs to id, class is used to associate a tag with a name.
7. id
The id attribute is used to set the unique name for the element & used for referring to it.
8. dir
Dir is a gives the direction of the text.
we can set this attribute of text direction
9. lang
The lang attribute is used for base language for the element.
10. language
Scripting language used for the element.
11. leftmargin
Specifies the leftmargin, which is the empty space to the left of the document.
12. link
Color of the hyperlinks that have not yet been visited.
13. marginheight
Gives the height of the top and bottom margins, in pixels.
14. marginwidth
Gives the width of the left and right margins, in pixels.
15. rightmargin
Specifies the rightmargin, which is the empty space to right of the document, in pixel.
16. scroll
Specifies the vertical scroll bar appears to the right of the document.
17. style
Specifies whether a vertical scrollbar appears to the right of the document. Default value for the attribute "yes" or "no".
18. text
Set the color of the text in the document.
19. title
Hold the additional information for the element.
20. topmargin
Specifies the topmargin, which is the empty space to top of the document, in pixel.
21. vlink
Color of the hyperlinks that have been visited.
The class attribute is used to indicate the class. It belongs to id, class is used to associate a tag with a name.
7. id
The id attribute is used to set the unique name for the element & used for referring to it.
8. dir
Dir is a gives the direction of the text.
we can set this attribute of text direction
- "ltr"-left to right
- "rtl"-right to left
9. lang
The lang attribute is used for base language for the element.
10. language
Scripting language used for the element.
11. leftmargin
Specifies the leftmargin, which is the empty space to the left of the document.
12. link
Color of the hyperlinks that have not yet been visited.
13. marginheight
Gives the height of the top and bottom margins, in pixels.
14. marginwidth
Gives the width of the left and right margins, in pixels.
15. rightmargin
Specifies the rightmargin, which is the empty space to right of the document, in pixel.
16. scroll
Specifies the vertical scroll bar appears to the right of the document.
17. style
Specifies whether a vertical scrollbar appears to the right of the document. Default value for the attribute "yes" or "no".
18. text
Set the color of the text in the document.
19. title
Hold the additional information for the element.
20. topmargin
Specifies the topmargin, which is the empty space to top of the document, in pixel.
21. vlink
Color of the hyperlinks that have been visited.

No comments:
Post a Comment